Yachting Monthly
- Digital edition


Wow, that was fast! Why trimarans are SO much fun to sail – and how to do it
- Theo Stocker
- February 13, 2024
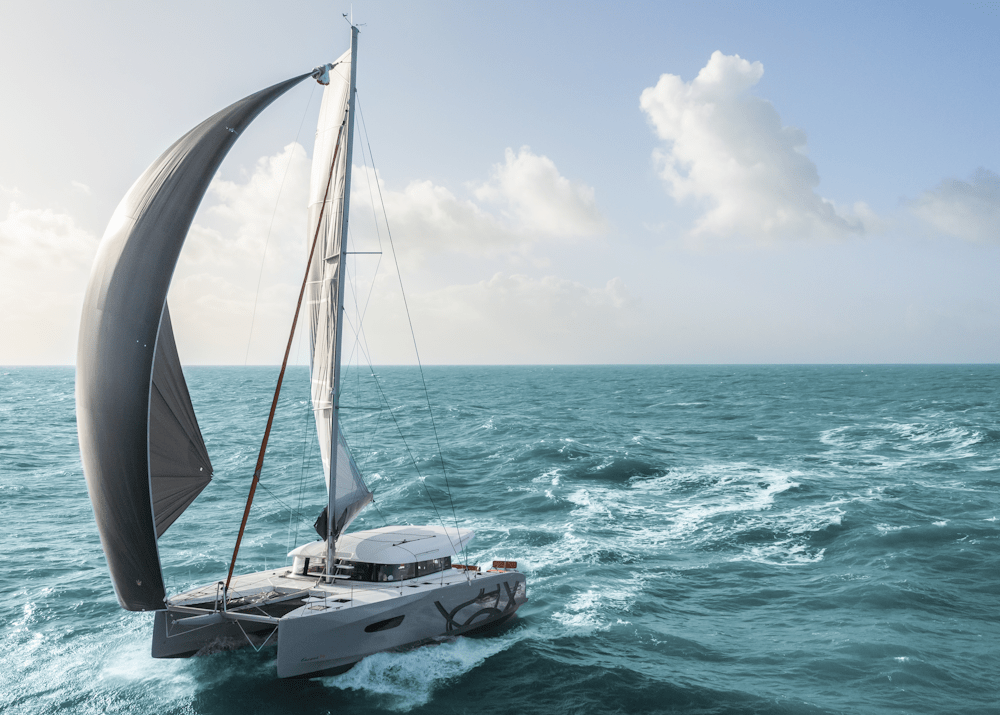
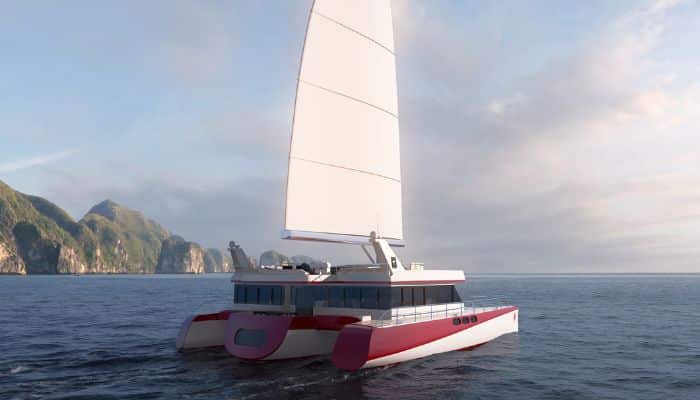
For their size, trimarans can punch well above their weight in speed, cruising potential and fun. Monohull sailor Theo Stocker gets to grips with how to handle one
Humans tend to gravitate into tribes of like-minded enthusiasts, enjoying the encouragement, support and sense of identity, while often looking askance at others; sailors at motorboaters, cruising sailors at racers, monohull sailors at raft, I mean, multihull sailors, and everyone looks askance at jet-skiers.
Large cruising catamarans (40ft now counts as a small one) are a world apart from monohull sailing, but there’s a sub-tribe of sailors dedicated to life on three hulls and builders such as Dragonfly, Corsair, Farrier, and Astus give them plenty of choice.
I’ve been sailing a 22ft (7m) Astus 22.5 this season, with just enough space for a family of four and a minimum of creature comforts. Thanks to her VPLP-designed hulls and 650kg all-up weight, we can sail upwind at 7-plus knots and downwind at over 10 knots with ease, all on a roughly even keel, while the kids play Duplo down below. It can also be beached and is towable behind a car.
Having, it seems, caught the trimaran bug, I wanted to get better at sailing and handling the boat, but my monohull sailing experience and habits were proving something of a hindrance, so we sought advice from some existing trimaran owners, and well as the UK’s top multihull sailors.
Much of the advice will apply to all multihulls , whether two or three-hulled, while other parts are just for small trimarans. I also found that brushing-up some of my rusty dinghy sailing skills helped get my head around what we were trying to do.
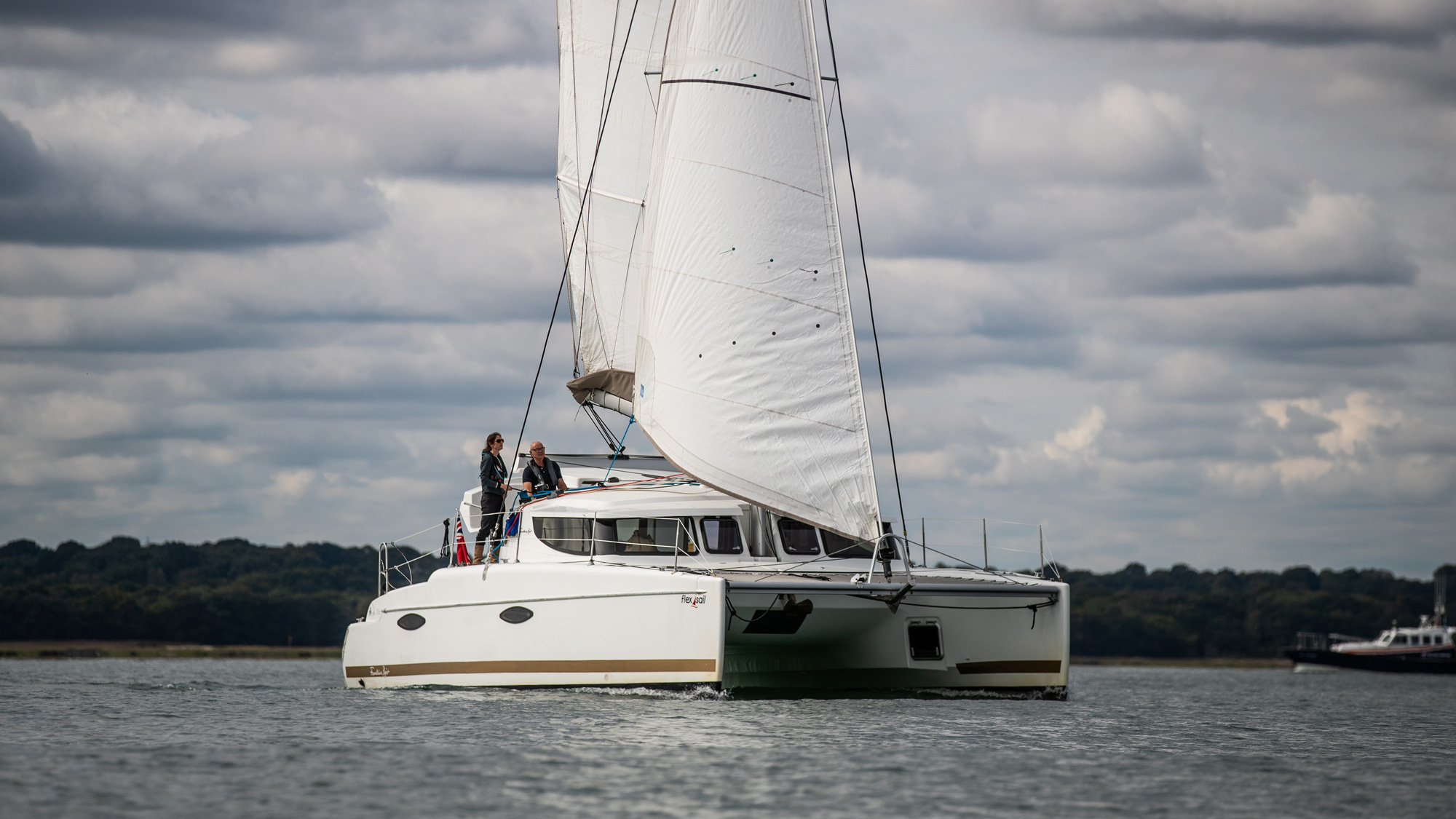
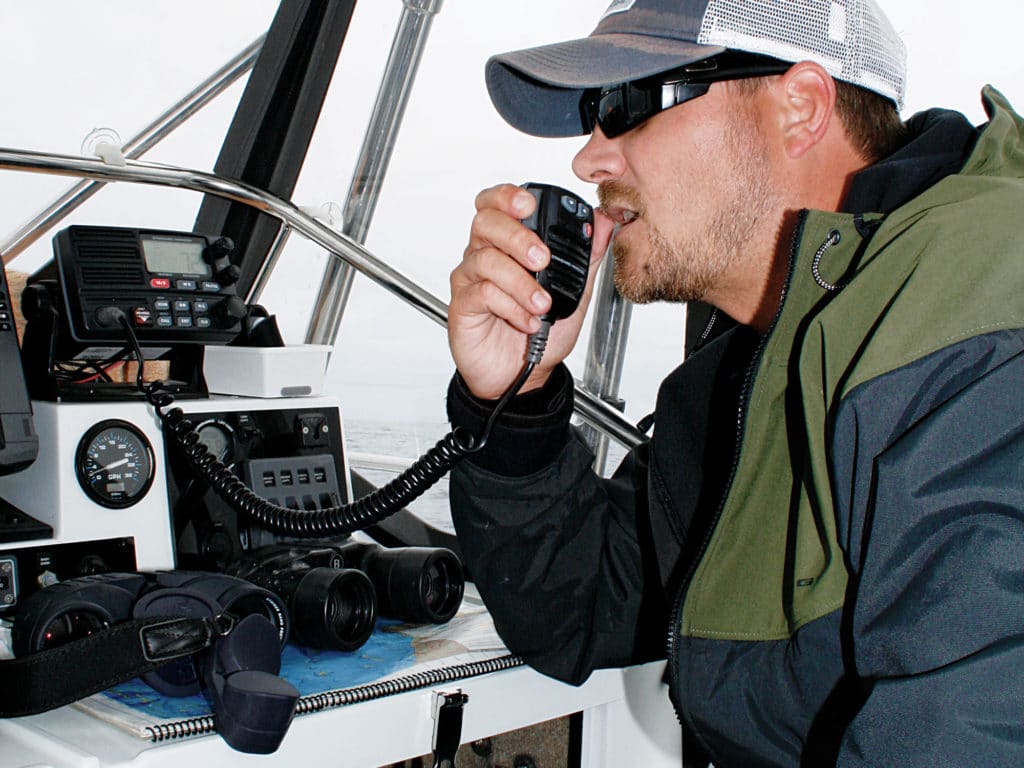
To try out our expert tips we went out sailing to see what difference they made. On the day, we got a solid Force 4-5 southwesterly, averaging 16 knots, but fluctuating between 12 and 20 knots true.

Blasting about on a sporty trimaran is a whole world of fun, but is much calmer than it looks
Trimaran sail trim
One of the biggest differences between a cruising monohull and a multihull is how the mainsail is trimmed. Leech tension on a yacht is often largely controlled by the kicker and the backstay, while the mainsheet sheets the mainsail in and out, predominantly controlling the angle of the boom to the centreline, and there may be a short traveller.
On a mulithull, however, there’s more than enough space for a good, wide traveller. Those who sail on performance monohulls will also be used to this. The sail shape is mainly controlled by the mainsheet, and the traveller then moves the boom towards or away from the centreline.
This is exaggerated on a multihull which has wide shrouds, swept well aft with no backstay, making space for a powerful square-top mainsail with full-length battens. There’s no backstay to bend the mast and flatten what is anyway a pretty rigid mainsail.

The mainsheet purchase creates enough power to control the leech of the square-top mainsail
Depowering a trimaran
Sailing on a monohull, heel and weatherhelm and eventually a broach give loads of warning that you’re pushing too hard. With straight hulls and little heel, those warning signs don’t really apply to multihulls.
In reality, however, there are a host of warning signals that it’s time to back-off; they’re just a bit different. Even then, there’s still a large safety margin before you get close to danger.
By way of reassurance, with the boat powered up on a beat, Hein, from Boats on Wheels, the boat’s owner, stood on the leeward hull and lent on the shrouds. Even as his feet got wet and the wind gusted at the top of Force 4, the boat didn’t bat an eyelid, thanks to the huge buoyancy of the floats.

Even with a person on the leeward float the boat was extremely stable
On the water – sail trim
My first inclination was to point the boat as high upwind as possible, pin the sails in and go for height. Doing that resulted in a not-terrible boat speed of 5-6 knots and a good pointing angle.
Free off by a handful of degrees however, and ease the sails just a smidge, and the speed leapt up to 8-9 knots – over 50% more; a huge increase. So, don’t pinch. If you had a decent chartplotter on board, you could find your optimum speed to angle using velocity made good (VMG).
I was also tempted to pinch in the gusts, but it’s better to hold your course and let the speed increase until the main needs easing.

On the wind, it’s time to get the boat fully powered up
If that’s the case, drop the main down the traveller an inch or two or ease some twist into the mainsail and it makes all the difference in the world, but not so far that the top battens fall away and invert – that really isn’t fast. Push too hard and the boat will slow down, largely from the drag of submerging the leeward float and crossbeams. If you’re still overpowered and the main is luffing, it’s time to reef. Downwind is different, but we’ll get onto that later.
After we put a reef in the main, our boat speeds upwind remained largely the same, and the boat was much happier. I came away feeling reassured that even a little trimaran like this would be pretty difficult to capsize, and there were always plenty of warning signs telling me to take my foot off the pedal a little.
Article continues below…

Catamaran sailing skills: Mooring and anchoring a multihull
How do you make an average passage speed of 7 knots, fit in three double cabins and a huge saloon…

Monohull or multihull: which is best for blue water?
As former editor of Yachting World, David Glenn has plenty of experience of both monohull and multihull cruising. Here he…
Tacking and gybing a trimaran
Everyone knows that multihulls don’t tack as well as monohulls. Straight hulls and wide beam don’t lend themselves to turning, especially when coupled with the displacement and fixed keels of big cats. Trimarans are a little easier, with a single central daggerboard to act as a pivot, and one or other of the floats will generally be clear of the water. On the downside, light displacement means that there isn’t much momentum to keep you going through the turn and plenty of windage to stop you.

On a trimaran the central daggerboard helps the boat to turn by providing a central pivot point that catamarans lack
Speed is your friend. Build speed up before the tack to give you as much momentum as possible. The helm needs to steer positively into and through the turn, and if necessary, keep the jib backed on the new windward side to help the bow through the wind. Don’t worry about scrubbing speed off, but you don’t want to get stuck in irons.
When it comes to gybing, speed is again key. The turning bit isn’t going to be an issue as you’ll be scooting along, but the faster you’re going, the less load there will be on the sails. The more you slow down, the more the true wind will pile up.
Trimaran sailing skills
Tacks took a bit of practice. It felt plain wrong to jab the tiller across the boat, slamming a big break on in the water but I ended up putting us through the tacks far too slowly, losing a lot of speed. A more aggressive approach worked better. On the Astus, the traveller was between me and the tiller, so the tiller extension needed to be swung around the stern behind the mainsheet onto the new side.
Similarly, old habits of controlling a gybe needed to be modified. With the asymmetric set, we were planing at well over 10 knots, and the ideal is to stay on the plane. Heading dead downwind and centring the main lead to a more violent manoeuvre than flying into the gybe as fast as possible and, as the boom was never that far out thanks to the apparent wind angle, it didn’t need much extra controlling.
Coming up onto the wind after the gybe helped the asymmetric around the front of the jib and to fill on the new side. Stay too deep and it’ll get blanketed by the main. Once we had built up some apparent wind, we could bear away again.

You’ll be on a course deep downwind before you know it, hitting speeds in the double digits
Downwind in a trimaran
Upwind cruising may be fun in a multihull, but bearing away and going with the wind is what it’s all about. Easily-driven hulls, a generous sailplan and light weight mean you can be up and planing, leaving displacement boats wallowing in your wake.
The big difference comes from apparent wind. If you’re in a boat that can do 15 knots downwind in 20 knots of true wind, the resulting wind angles can really mess with your head.
To get going then, says Brian Thompson, ‘Use those leech tell-tales again when sailing downwind and reaching to set the correct twist through the mainsheet, and use the traveller to set the correct angle of the whole sail to the wind.’
As the wind and your speed builds, bear away and trim the main accordingly.
In theory, you shouldn’t need to ease the traveller at all, but you may need to if you want to sail deep downwind. As the gust fades, you’ll find the boat slows down, so you can come back up towards the wind a little to pick up some more breeze, and then bear away as you accelerate again.

Bear away as the boat accelerates. Your course will be something of a slalom as you look to keep a consistent wind angle
This results in something of a ‘slalom’ course, and will also be accentuated if you’re sailing down waves, but that’s all quite normal for apparent wind sailing. Ultimately, you’re looking for a consistent apparent wind angle, even if the resulting wake isn’t straight.
It’s worth remembering that apparent wind reduces the felt effect of the wind, so you need a sailplan to suit the true, not apparent wind speed.
I found that the boat was more sensitive to having a balanced sailplan and trim downwind than upwind, largely because you’ve got almost double the canvas up, with the bowsprit as an extra lever. When weather helm built, I needed to ease the mainsheet to increase twist to depower so that I could bear away. I must admit, getting the boat balanced, sailing fast and light on the helm at 15 knots was something I came away feeling I needed more practice at.
Reviewing the images, I suspect the asymmetric was sheeted in too hard, with too much twist in the main.

Getting a float fully submerged is when it’s time to back off
On the water
Unfurling the gennaker worked best on a beam reach, giving plenty of airflow over the sail to help it fully unfurl. This was also roughly the fastest point of sail, ideal for getting up some speed for apparent wind sailing. We mostly had the sails set for a close reach, even when we were beyond 120º off the true wind on a broad reach.
It was possible to soak deeper downwind, but lose the apparent wind benefit downwind and our speed dropped off dramatically, prompting us to point a bit higher to find some more speed.
As the boat powered up, it paid to hold a slightly higher angle than I would have done in a monohull for the boat to properly take off and get up into double digit speeds – topping out at 15 knots. Lymington to Cowes would have taken us just half an hour at that speed. It’s easy to give yourself a heck of a beat back!
We were sailing on a pretty flat day, so didn’t have to contend with any waves to speak of. On the recent RTI this is what caused the capsizes of at least two multis, a sobering reminder that you need to sail much more conservatively in lumpier conditions.

The bows want to point downwind, so a stern-first approach works with rather than against the boat
Coming alongside
A 650kg boat with no draught and plenty of windage feels dreadfully skittish when manoeuvring in confined spaces. Straight hulls with no forgiving curves and fragile-looking sharp bows make berthing tricky. You’ve got a couple of advantages on your side, however. In the Astus, the floats are at pontoon height making stepping off easy.
Whether you have an engine in each hull of a cat, or one in the central hull of a tri, there’s also a lot more leverage to play with to turn the boat and drive her on or off the pontoon. A steerable outboard gives you even more options.
If the boat has a lifting keel or daggerboards, put them down if there’s enough depth to give you a pivot and to resist drifting. Think about getting corners onto the pontoon, rather than putting the boat alongside. On tris, you won’t be able to get to the bow to fend off as it’s too narrow. You can rig a fender up forwards on a line, and two fenders are enough on the flat sides.

Steering with the outboard towards the pontoon will drive the stern in more; steer away to drive the bow in more
Offshore wind
Coming onto the pontoon with wind blowing off, it worked well coming in stern first. If there’s a tide running, you’ll want to be heading into the tide, so find a spot down wind and down tide to start your approach so you come in at an angle.
On our first attempt we had a bit of tide under us to start with so we came in at a much steeper angle, almost 90º, although this worked out OK in the end.
The crew could then step ashore, taking a line from the stern quarter round a cleat.
Drive forwards against the line and the bow will obediently drive up towards the pontoon, bringing you flat alongside. Getting off was simple, releasing the bowline, and allowing the bow to swing out the before slipping the stern line.

Coming in astern and stopping upwind of the berth meant the bows blew towards the pontoon far to quickly
Onshore wind
Getting onto and off a pontoon with onshore wind proved rather trickier. On our first attempt we came in stern first. The issue was that once we were just upwind of our desired berth and stopped, we lost steerage and the bow immediately blew off with alarming speed towards the pontoon.
Going ahead would only increase the force of the impact, while going astern only increased the bow’s sideways drift. I managed to back out without smashing the bow, but only just, and ended up awkwardly stern to the wind with the bows pointing at the pontoon.
On our second attempt we came in bows first but having aimed at the berth, I had to motor the stern to leeward to stop the bow hitting, making for a rather forceful coming alongside.
On take three, I came in forwards and began ferry gliding towards the berth early, keeping the bows to windward of the stern. Being able to steer with the outboard meant I could go ahead to keep the bow up, and go astern with the engine pulling the stern down toward the pontoon. In this way, it was possible to come in pretty well controlled and parallel to the berth.

To get out, motoring astern against a bow line pulled the entire boat clear before slipping the line
Leaving was a different proposition all together, as I didn’t want to drag the bow along the pontoon, or to drive hard onto it to spring off. Instead, we rigged a slip-line from the forward cross beam. Going astern against this, and then turning the engine towards the wind, I could pull the stern, and the rest of the boat, out and away from the pontoon.
Keeping power on astern, once we’d reached a decent angle, we slipped the line and went astern, finding steerage way almost at once, with the bow following obediently in our wake with more control than I had anticipated.
Whether the wind is blowing onto, or off the pontoon, you want the engine to be driving or pulling the boat off the pontoon with a line on the corner you are going away from. That way you avoid point-loading fine ends where it’s hard to fender.

You’ll want a bridle to reduce swinging, but keep the pick up lines on the bow as backup
Anchoring and mooring a trimaran
While mooring a catamaran is complicated by the lack of a central bow, things should be simpler on a trimaran, and they are, mostly. Picking up a mooring buoy from the main hull bow with a low freeboard and dropping the pick-up line onto a cleat is easier even than a monohull.
The bow may be narrow, but for any lines that pass through a ring on the buoy, you still need to take it back to the same cleat to avoid chafe. That should be it, but windage from the two extra bows and the lack of keel mean the boat can dance merrily around the mooring buoy in a breeze.

Rig the bridle so the buoy sits to one side to stabilise the boat
In practice, we found that a trimaran benefits from a mooring bridle in the same way that a catamaran does. It can’t be rigged from the floats’ bows, as there are no mooring cleats, so a line passed around the outboard ends of the forward beams gave a pretty good angle, again with long lines passed through the mooring and back to the same side. The main pick-up lines stay as a safety backup.
The other trick is to rig the bridle asymmetrically so that the buoy sits to one side or the other, just enough to not be dead head to wind, making it much more stable in the wind.
On the plus side, the lack of draught or keel means that you’ll nearly always be lying head to wind, so the cockpit remains nice and sheltered whatever the tide’s doing.
We ran out of time on the day to try anchoring, but rigging a bridle, effectively a long snubber to a point on the anchor chain in a similar way wouldn’t be tricky.
If you needed not to swing, or to behave more like deeper boats nearby, hanging a bucket over the stern can help, or there’s always anchoring with a kedge, either out ahead in a V, or in line astern.
Enjoyed reading this?
A subscription to Yachting Monthly magazine costs around 40% less than the cover price .
Print and digital editions are available through Magazines Direct – where you can also find the latest deals .
YM is packed with information to help you get the most from your time on the water.
- Take your seamanship to the next level with tips, advice and skills from our experts
- Impartial in-depth reviews of the latest yachts and equipment
- Cruising guides to help you reach those dream destinations
Follow us on Facebook , Twitter and Instagram.

The global authority in superyachting
- NEWSLETTERS
- Yachts Home
- The Superyacht Directory
- Yacht Reports
- Brokerage News
- The largest yachts in the world
- The Register
- Yacht Advice
- Yacht Design
- 12m to 24m yachts
- Monaco Yacht Show
- Builder Directory
- Designer Directory
- Interior Design Directory
- Naval Architect Directory
- Yachts for sale home
- Motor yachts
- Sailing yachts
- Explorer yachts
- Classic yachts
- Sale Broker Directory
- Charter Home
- Yachts for Charter
- Charter Destinations
- Charter Broker Directory
- Destinations Home
- Mediterranean
- South Pacific
- Rest of the World
- Boat Life Home
- Owners' Experiences
- Conservation and Philanthropy
- Interiors Suppliers
- Owners' Club
- Captains' Club
- BOAT Showcase
- Boat Presents
- Events Home
- World Superyacht Awards
- Superyacht Design Festival
- Design and Innovation Awards
- Young Designer of the Year Award
- Artistry and Craft Awards
- Explorer Yachts Summit
- Ocean Talks
- The Ocean Awards
- BOAT Connect
- Between the bays
- Golf Invitational
- BOATPro Home
- Superyacht Insight
- Global Order Book
- Premium Content
- Product Features
- Testimonials
- Pricing Plan
- Tenders & Equipment
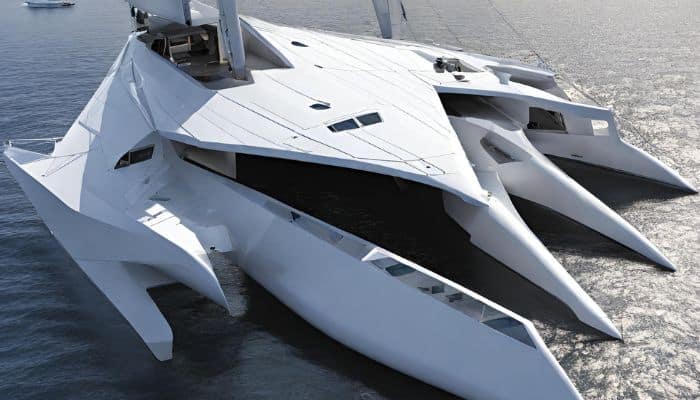
12 of the coolest multihull superyachts
The market for multi-hull superyachts has skyrocketed in recent years as owners begin to favour the high volumes and superlative stability on offer. Once the novelty of a small group of owners, a recent slew of multi-hull concepts and the success of shipyards such as Sunreef has confirmed that two and three-hulled superyachts are well and truly on the up. We remember some of the most ground-breaking multi-hull launches...
White Rabbit
One of the coolest launches of 2018, the 84 metre White Rabbit is the largest trimaran in the world. She was built in fibreglass by Australian Yard Echo Yachts with exterior design by Sam Sorgiovanni and naval architecture by One2Three. White Rabbit was delivered to an experienced owner who owns a number of other multihull superyachts, including a 51 metre shadow catamaran, also built by Echo Yachts, which will be used as a support vessel; for the 84 metre trimaran.
More about this yacht
Inspired by Game of Thrones, the 66 metre shadow catamaran Hodor is a support vessel used to carry all the toys and tenders for her mothership. The vessel is fully custom and was designed by Incat Crowther. Hodor boasts five tenders, including a 17 metre chase boat and a 388 Skater powerboat with a top speed of 165 knots. Other toys include nine Jet Skis, two Yamaha ATCs, four Yamaha TW200 trail motorcycles and a three-person submarine.
A true icon, Adastra was launched in 2012 by Australian yard McConaghy Yachts . With a length of 42.5 metres and a sleek Kevlar and GRP exterior, this space-age design is every bit as out-of-this-world as its name suggests. Made for exploring, an impressive 10,000 nautical mile range means she can cross the Atlantic twice before needing to refuel. A shallow draft of 1.2 metres allows her to access hard to reach anchorages and shallow bays too.
In 2011, Hemisphere was launched as world’s largest sailing catamaran with an LOA of 44.2 metres - and she remains so to this day. Built for American owners who had previously chartered a catamaran in the Caribbean, this British yacht was a bespoke project by Pendennis . Fully kitted out for diving, Hemisphere ’s port hull contains a dive centre capable of refilling both air and Nitrox tanks.
Yachts for charter
Royal falcon one.
The 41.4 metre Royal Falcon One is a quirky catamaran launched in 2019. She was designed by Singapore-based Royal Falcon Fleet in collaboration with F.A Porsche Design Studio and built in Sweden by Kockums. Accommodation is for up to 10 guests in five spacious cabins, including a full beam master suite with its own private deck space. Crew are housed in the two hulls.
Yachts for sale
Launched in 2015, Spirit is a 35 metre New Zealand Yachts powercat featuring Ken Freivokh interiors and naval architecture by Bakewell-White Design . A perfect example of how catamarans can help to maximise the living space available, Spirit has the interior volume you might expect from a 45 metre monohull. Her unconventional looks will make her stand out from the crowd in her new home of Australia, but Spirit is just one of many striking multihull superyachts to have hit the water in recent years.
Pilar Rossi
Formula One racing legend Nelson Piquet’s yacht Pilar Rossi was built in Turkey as a modest 33 metre Alucraft motor yacht. But his uncle, a Brazilian naval architect, helped Piquet convert her into a 64 metre sailing trimaran by adding outriggers and two masts. The reborn trimaran can accommodate up to 18 guests.
Galaxy of Happiness
Unveiled to the world in May 2016, Galaxy of Happiness is one of two 53 metre trimarans to be launched by Latvian yard Latitude Yachts . This multihull superyacht is built from a GRP and carbon fibre composite and is capable of a top speed of 30 knots. The interior, designed by Latitude Yachts and Jean-Jacques Coste , features an owner’s cabin and two guest cabins.
Launched in 2004, this Chinese catamaran from Pride Mega Yachts may look like a vision of the future, but the inspiration for Asean Lady is actually ancient. The twin hulled 88.15 metre yacht is based on the proa design that has been used for more than 2,000 years to build fishing boats in the Pacific region. Her stability was put to the test in December 2004 when she survived the Indian Ocean tsunami while moored off Phuket.
Flexibility is the key word that informed the design of the 33.7 metre Quaranta . Launched at Turkish yard Logos Marine in 2013, this catamaran superyacht features the kind of interior volume more commonly associated with a 40 metre yacht. All six guest suites are located on the main deck and the absence of structural bulkheads means that they can easily be reconfigured. This innovative system helped Quaranta to win the catamaran award at the 2014 World Superyacht Awards .
Sponsored listings
Newest Posts
- Boat Selection: Budget Considerations
- Outboard Engine Repair and Maintenance: Everything You Need to Know
- Refinishing Decks and Topsides: A Restoration Work Guide
- Reviews and Ratings: What You Need to Know
- Inflatables and tenders
- Ribs and rigid inflatables
- Inflatable sailboats
- Inflatable kayaks and canoes
- The Art of Boat Building: A Guide from an Expert
- The Ins and Outs of Boat Shipping Companies
- Racing sailboats
- Houseboats and yachts
- Motor yachts
- Sailing yachts
- Luxury houseboats
- Personal watercrafts
- Ski and wakeboard boats
- Fishing boats
- Cabin cruisers
- Pontoon boats
- Choosing a boat type
- Identifying your needs
- Power or sail?
- Budget considerations
- Types of propulsion systems
- Selecting a dealer or broker
- Checking references
- Negotiating pricing and financing
- Researching boats
- Comparison shopping
- Reviews and ratings
- Test drives and sea trials
- Design and planning services
- Hull design and engineering
- Cabin design and layout
- Materials and construction services
- Woodworking and joinery services
- Metal fabrication services
- Finishing services
- Painting and varnishing services
- Upholstery and canvas services
- Electrical system repair services
- Wiring and rewiring services
- Electrical system diagnostics and troubleshooting
- Engine repair and maintenance services
- Inboard engine repair and maintenance
- Outboard engine repair and maintenance
- Structural repairs and maintenance services
- Deck repairs and maintenance services
- Hull repairs and maintenance services
- Transport options for boats
- Shipping a boat by ocean freight or air freight
- Towing a boat by trailer or truck
- Use A1 Auto Transport Boat Transport Services And Claim 15% Off
- Logistics for boat transport
- Documentation requirements for boat transport
- Insurance requirements for boat transport
- Boat unloading services
- Unloading boats from air freight containers
- Unloading boats from ocean freight containers
- Replacement parts
- Replacement outboard motors
- Replacement inboard motors
- Replacement electrical components
- Preventive maintenance services
- Cleaning and waxing the hull
- Cleaning and polishing the topsides
- Inspecting the rigging
- Repair services
- Engine repairs
- Electrical system repairs
- Hull repairs
- Assessing the condition of the boat
- Testing the electrical systems
- Identifying damage to the hull
- Inspecting the riggin
- Restoration work
- Rewiring the electrical systems
- Refinishing decks and topsides
- Replacing rotten woodwork
- Finishing touches
- Painting the hull
- Installing new upholstery
- Varnishing woodwork
- Trimarans - Exploring the Unique Three-Hulled Sailboat
Have you ever heard of a trimaran? It's a unique type of sailboat with three hulls, and it's quickly becoming one of the most popular sailing vessels out there. Trimarans offer a special kind of sailing experience, combining the stability of a catamaran with the speed and agility of a monohull sailboat. In this article, we'll explore the history, design, and uses of trimarans, and discover why they're quickly becoming the go-to choice for sailing enthusiasts. If you're interested in purchasing a trimaran, you may be wondering about the Florida boat shipping cost .
The history of Trimaran sailboats dates back to the early 19th century when they were first developed by the British Royal Navy. Trimarans are unique in that they have three hulls instead of the traditional two-hulled design of most sailboats. They offer a number of advantages over other boat types, including increased stability in rough waters, faster speeds than monohulls, and a greater range of motion for the captain. However, trimarans come with a number of drawbacks, such as their higher cost and increased vulnerability to damage. One of the most famous trimarans is the US-built 'Defiance', which was designed by naval architect Reuel Parker and first launched in 1887. Defiance was one of the earliest trimarans to be used for recreational sailing, as well as for competitive racing.
Types of Trimarans
Trimaran construction, sails and rigging, safety considerations, the disadvantages of trimarans.
This can make them prohibitively expensive for recreational sailors who may not have the budget to buy or maintain a trimaran. Trimarans are also more vulnerable to damage due to their multiple hulls. If one of the hulls is damaged, the entire boat can become unstable and dangerous. This makes them more risky to sail in rough conditions than monohulls. Trimarans are also more complex than monohulls in terms of rigging and sailing. They require more experience and skill to operate, making them better suited for experienced sailors.
The Advantages of Trimarans
Trimarans also offer increased speed compared to monohulls, due to their decreased drag in the water. This makes them particularly attractive for competitive racing, as they can outpace monohulls in most conditions. Trimarans are also much more maneuverable than other boats, allowing them to quickly turn and change direction. In addition, trimarans offer increased space aboard compared to monohulls.
Cruising Trimarans
Construction and rigging.
The three hulls on a trimaran are typically connected by a central frame, and are made of lightweight yet durable materials such as fiberglass or aluminum. This allows for a lighter and more maneuverable sailing experience. When it comes to rigging and sails, trimarans use the same basic principles as other sailboats. The sails used on trimarans are mainly spinnakers, jibs, mainsails, gennakers, and staysails.
In addition, a trimaran needs additional rigging and gear such as halyards, sheets, and running rigging. Trimarans can also be equipped with additional equipment such as anchors, fenders, and radios. This can help improve safety and performance while sailing. In conclusion, trimarans offer a unique sailing experience due to their three-hull design.
They require the same basic rigging and sails as other sailboats, but also have additional needs for extra equipment. With the right rigging and gear, trimarans can be used for recreational sailing as well as competitive racing events. Trimarans are a unique and exciting type of sailboat that offers some distinct advantages over monohulls. They have three hulls instead of two, and provide greater stability and agility than other boat types.
Trimarans are used for both recreational sailing and competitive events, and require more crew members than monohulls. The construction and rigging of trimarans is also more complex than other boat types, and safety considerations should always be kept in mind. Therefore, if you're looking for a unique sailing experience, a trimaran could be the perfect choice. In conclusion, trimarans offer an exciting and unique sailing experience, with many advantages over traditional monohulls. They are suitable for both recreational sailing and competitive events, but require additional crew members and safety considerations.
If you're looking for a unique sailing experience, trimarans could be the perfect choice.
- Ribs and Rigid Inflatables: What You Need to Know
- Daysailers: An Informative Overview
- Identifying Your Needs: Choosing the Right Boat Type
- Cruisers: An In-Depth Look at One of the Most Popular Sailboat Types
- Catamarans: Exploring the Versatile Boat Type
- Everything You Need to Know About Bowriders
Understanding the Differences between Power and Sail Boats
- Motor Yachts: A Comprehensive Look at the Luxury Boating Option
- Personal Watercrafts: A Comprehensive Overview
- Sailing Yachts: An Overview
- Everything You Need to Know About Racing Sailboats
- Discovering the World of Luxury Houseboats
- Everything You Need to Know About Ski and Wakeboard Boats
- Everything You Need to Know About Fishing Boats
- Inflatable Sailboats: Everything You Need to Know
- Inflatable Kayaks and Canoes: Everything You Need to Know
- Cabin Cruisers: An In-depth Look at Powerboats
- Pontoon Boats: Everything You Need to Know
- Everything You Need To Know About Catamarans
- Checking References for Boat Selection and Broker Selection
- Comparing Boats: A Comprehensive Overview
- Exploring Hull Design and Engineering
- Wiring and Rewiring Services for Boats
- Inboard Engine Repair and Maintenance
- Types of Propulsion Systems: An Overview
- Diagnosing and Troubleshooting Electrical Systems
- Deck Repairs and Maintenance Services: Everything You Need to Know
- Woodworking and Joinery Services: An Overview
- Painting and Varnishing Services: A Comprehensive Overview
- Metal Fabrication Services - A Comprehensive Look
- Shipping a Boat - Choosing Between Ocean Freight and Air Freight
- Documentation Requirements for Boat Transport
- Negotiating Pricing and Financing for Boat Selection
Cabin Design and Layout Explained
- Everything You Need to Know About Upholstery and Canvas Services
- Towing a Boat by Trailer or Truck
- Unloading Boats from Air Freight Containers
- Replacement Outboard Motors: Everything You Need to Know
- Cleaning and Waxing the Hull: A Comprehensive Guide
- Testing the Electrical Systems: An Overview
- A Comprehensive Overview of Engine Repairs
Rewiring Electrical Systems for Boat Restoration
- Cleaning and Polishing the Topsides
- Insurance Requirements for Boat Transport
- Painting the Hull: A Comprehensive Overview of All Aspects
- Test Drives and Sea Trials: A Comprehensive Overview
- A Comprehensive Overview of Electrical System Repairs for Boats
- How to Repair Your Boat Hull
- Inspecting the Rigging: A Comprehensive Guide
- Replacement Inboard Motors: What You Need to Know
- How to Replace Rotten Woodwork
- Unloading Boats From Ocean Freight Containers
- Identifying Damage to the Hull - A Comprehensive Guide
- Inspecting the Rigging: Assessing the Condition of the Boat
- Hull Repairs and Maintenance Services: Everything You Need to Know
- Replacement Electrical Components: A Comprehensive Overview
- Installing New Upholstery: A Step-by-Step Guide
- Varnishing Woodwork: A Comprehensive Guide
New Articles

Which cookies do you want to accept?
Yachting World

Expert tips: how to sail multihulls downwind in big breezes

5 of the best new ocean cruising catamarans for 2024

The best specialist yachts: new and interesting designs

Best catamaran and multihull: We sail the very best yachts on two and three hulls

Caudrelier wins first ever solo round the world race in foiling Ultim

HH44 review: Taking fast multihull cruising to another level

Nautitech 48 Open first look: last design of legend Marc Lombard

Some of the world’s biggest, coolest catamarans go racing
How to buy a multihull.

European Yacht of the Year 2019: Best multihulls

Performance cruisers: the best new catamarans for racing and fast cruising 2018

Fast Bluewater Cruisers: the best new performance bluewater catamarans on the market 2018

Family cruisers: The best multihulls for space and comfort at sea
How to charter a multihull.

Buy to let guide: owning and chartering a catamaran – everything you need to know about how to make it work
Catamaran sailing techniques.

How to get a multihull ready for bluewater sailing

Catamaran cruising: everything you really need to know

Catamaran Sailing Techniques: Everything you need to know

Catamaran Sailing Techniques Part 2: Handling under power – with Nigel Irens

Catamaran Sailing Techniques Part 3: Anchoring and picking up a mooring – with Nigel Irens

Catamaran Sailing Techniques Part 4: Sailing a cat upwind – with Nigel Irens

Catamaran Sailing Techniques Part 5: sailing a cat downwind – with Nigel Irens
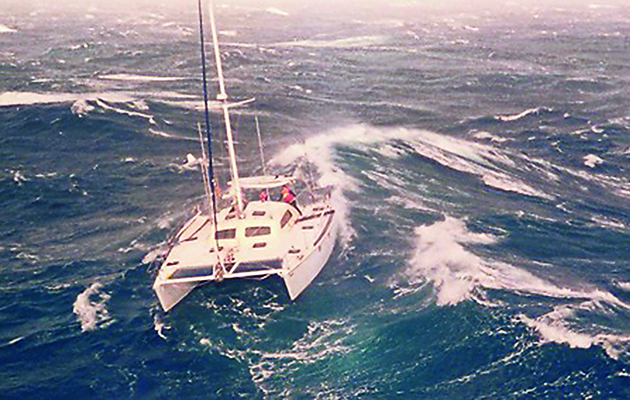

Catamaran Sailing Techniques Part 6: Coping with heavy weather – with Nigel Irens
Catamarans: A Complete Guide to Multihull Boats
Catamarans have been a part of sailing history for centuries and continue to be popular for their stability, spaciousness, and performance. Developed by various cultures around the world, the principles of catamaran design have evolved over time to become optimized for both pleasure cruising and racing. This complete guide will help you understand the essentials of catamarans, their unique characteristics, and how to choose the right one for your needs.

From the basic concepts of multihull design, performance, and handling, we will explore the advantages and benefits of a catamaran in terms of safety and comfort on board.
Along the way, we will discuss maintenance considerations, distinctive catamaran brands and models, and how a catamaran lifestyle can compare to more traditional sailing options .
Finally, we will provide learning resources and frequently asked questions tailored to both seasoned sailors and newcomers to the world of catamarans.
Key Takeaways
- Catamarans are known for their stability, spaciousness, and performance
- This guide covers aspects like design, handling, safety, and choosing the right catamaran
- Resources and frequently asked questions provide additional insights for potential catamaran owners
Understanding Catamarans
Design Characteristics
Catamarans are known for their unique design, which features two parallel hulls connected by a deck. This design provides several advantages over traditional monohull boats, such as stability and speed.
With their wide beam, catamarans have a reduced risk of capsizing and can access shallow waters due to their shallow drafts 1 .
One of the notable aspects of a catamaran is its twin hulls, which offer increased living space and comfort compared to a monohull. Additionally, catamarans are often favored by recreational and competitive sailors for their excellent maneuverability 2 .
The materials used for constructing catamarans range from wood to fiberglass, and even aluminum for high-performance vessels. Aluminum catamarans are known for their strength, lightweight structure, and resistance to corrosion 3 .

Hulls and Construction
The hulls in a catamaran are crucial to its stability and performance. These hulls help distribute the weight evenly across the water surface, minimizing drag and allowing for smoother sailing.
In general, the hulls can be categorized into two types:
- Symmetrical Hulls : The hull shape is similar on both sides, which enhances balance and stability in various sailing conditions.
- Asymmetrical Hulls : One side of the hull is designed differently than the other, which can be advantageous when sailing upwind.
The construction materials used in building catamaran hulls also play a vital role in the boat's performance and durability. Common materials include:
- Fiberglass : A popular choice due to its lightweight, strength, and ease of maintenance.
- Wood : Traditional material that offers a classic look, but requires more maintenance than fiberglass or aluminum.
- Aluminum : Lightweight and strong, aluminum is an excellent choice for high-performance catamarans 4 .

Multihulls vs Monohulls
There's often a debate between the benefits of multihull boats, such as catamarans or trimarans, and monohull boats. Here are some key differences between the two:
- Stability : Due to their wide beam and reduced heeling, catamarans offer improved stability compared to monohulls. This makes them an attractive option for those who want to avoid seasickness or feel more comfortable on the water 5 .
- Speed : Multihull boats are known for their speed, which results from their ability to minimize drag and maintain a level sail.
- Living Space : Catamarans and other multihulls generally have more living space, as both the hulls and the connecting deck can be utilized for accommodation and storage.
- Maneuverability : While monohulls are known for their agility and ability to point close to the wind, catamarans can still offer exceptional maneuverability when properly sailed 6 .
Performance and Handling
Speed and Efficiency
Power catamarans have gained popularity for offering a unique combination of speed, efficiency, and stability. Their dual-hull design allows for less water resistance, which directly translates to higher speeds and better fuel efficiency compared to traditional monohull boats.
In addition, the wide beam provided by the two hulls ensures a stable ride even at higher speeds. This makes power catamarans ideal for cruising, fishing, and watersports ( Boating Beast ).
Sailing Dynamics
When it comes to sailing catamarans , the performance is affected by factors such as keel, rudders, mast, and sails.
Their wide beam and dual-hull design provide inherent stability and reduced heeling effect, making them less likely to capsize compared to monohulls.
I should also note that catamarans have a shallow draft, which gives them the ability to access shallow waters that may be off-limits to other boats ( Navigating the Waters ).
In my experience, the lighter weight of a catamaran and its aerodynamic design can contribute to remarkable sailing performance under different wind conditions.
The larger sail area relative to hull weight allows them to harness more wind power, further enhancing their speed and agility on the water.
Maneuvering and Docking
Maneuvering and docking a power catamaran involves understanding its unique handling characteristics.
The presence of two engines in separate hulls allows for more precise control in confined spaces such as marinas.
The maneuverability of these boats is typically improved by the use of dual rudders that are located close to each powered hull for efficient steering ( BoatUS ).
When docking under power, I find it helpful to carefully assess the wind and current conditions beforehand.
This is because catamarans can be more sensitive to windage due to their larger surface area above the waterline.
By understanding how these forces may affect the boat, I can make adjustments to my approach and successfully dock the catamaran without any incidents.
Safety and Comfort on Board
Safety Features
Safety is a top priority when sailing any type of vessel, including catamarans. A well-built catamaran offers several features aimed at ensuring the safety of those onboard.
First, catamarans have inherent stability due to their wide beam and twin hull design . This makes them less prone to capsizing than monohull boats. This stability allows me to confidently navigate various water conditions .
In addition to stability, catamarans are designed with positive buoyancy, making them almost unsinkable . Of course, safety equipment such as lifejackets, flares, and first aid kits should always be onboard and well-maintained.
Furthermore, you should also stay updated on weather conditions, avoid sailing in high-risk areas, and learn your boat's safe sail limits.
Living Spaces and Comfort
When it comes to living spaces, I value comfort and practicality as essential features for my time on the water. Catamarans offer a unique advantage in this regard, as their dual hulls create spacious living areas.
Most catamarans are designed with separate cabins in each hull, allowing for privacy and comfort when sleeping. Additionally, these boats typically feature shallow drafts , which means I can access shallow waters and anchor close to shore.
The main living area, or salon, is situated on the bridge deck between the hulls. It usually includes a seating area, a dining table, and a galley (kitchen). Large windows provide ample natural light and panoramic views, making the space feel open and bright. Some catamarans even have the option for an additional living area on the upper deck where you can enjoy the sun and breeze.
One aspect of catamaran living I truly appreciate is the ample storage available. Each cabin typically has built-in storage spaces for clothes, gear, and personal items. There are also designated areas for equipment such as spare sails, tools, and water toys. This makes it easy for me to keep my belongings organized and make the most of my time on the water.
Maintaining a Catamaran
Routine Maintenance
In order to keep my catamaran in the best possible shape, I make sure to perform routine maintenance tasks. These tasks are essential to extend the life of the components and ensure smooth sailing:
- Cleaning : Regularly cleaning the deck, hulls, and sails prevents buildup of dirt, algae, and other debris that could affect performance.
- Inspection : Periodically inspecting my catamaran allows me to detect any potential issues before they become significant problems. I pay close attention to the rigging, sails, and lines on my boat.
- Lubrication : Keeping all moving parts lubricated is vital to prevent friction and wear on components such as winches and pulleys.
- Antifouling : Applying antifouling paint to the hulls of my catamaran helps prevent the growth of marine organisms that can damage the boat and reduce its speed. Make sure to do this at least once a year.
Dealing with Wear and Tear
Despite my best efforts to keep my catamaran well-maintained, wear and tear is inevitable. Here's how I deal with common issues that could arise from regular use:
- Repairs : When I notice signs of wear on sails, lines, or rigging components, I make it a priority to repair or replace them promptly. Neglecting these issues can lead to more significant problems and affect the boat's performance.
- Hull maintenance : If I find dents, scratches, or stiff rudders on my catamaran's hulls, I address them immediately. Repairing any damage not only ensures smooth sailing but also prevents further issues from developing.
- Sail care : Over time, my sails can become stretched, torn, or damaged due to exposure to sun, wind, and saltwater. Regularly inspecting them for signs of wear and making any necessary repairs or replacements helps maintain optimal performance.
- Rust and corrosion prevention : Since my catamaran is made of various metal components, I need to protect them from rust and corrosion. I routinely check for signs of corrosion and apply anti-corrosive treatments when needed.
Catamaran Brands and Models
High-Performance Models
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in high-performance catamarans. I have seen a variety of brands and models that have impressed me with their performance capabilities. One notable brand is Fountaine Pajot , which has a long history of producing a range of sailing catamarans and power catamarans. Some of their popular models include the Tanna 47 and the Bali 4.4 .
Another high-performance catamaran I've come across is the Leopard 40 . Known for their speed and exceptional handling in various conditions, the Leopard brand started with sailing catamarans and has since expanded to include power catamarans. Their models range from 40 to 53 feet long, offering both power and luxury for those looking for a thrilling experience on the water.

Cruising Catamarans
When it comes to cruising catamarans, the Lagoon brand is synonymous with luxury and comfort. With a range of sailing catamarans from 40 to 70 feet long, Lagoon offers spacious catamarans for extended bluewater cruising. Their 60- and 70-foot power catamarans are equally impressive, providing ample living space and smooth sailing experiences.
I've also found the Aquila 42 PC to be a remarkable cruising catamaran. With a focus on design and innovation, Aquila has produced catamarans perfect for exploring the open sea with friends and family. Their spacious, stable designs allow for a more enjoyable and serene journey, ensuring you arrive at your destination comfortably.
The Catamaran Lifestyle
Anchoring and Cruising
I find catamarans to be a fantastic choice for cruising and anchoring , which is a critical part of living the catamaran lifestyle . Catamarans have several advantages when it comes to anchoring and cruising, such as:
- Stability : Due to their wide beam and twin hulls, catamarans remain stable during anchoring, which reduces the risk of seasickness.
- Shallow draft : Thanks to their shallow draft , catamarans can anchor close to shore, enabling better access to protected coves and more beautiful beaches.
- Speed : Despite their large size for cruising vessels , catamarans are generally faster than monohulls. This is a result of their slim hulls and reduced water resistance.
When it comes to anchoring, catamarans can make use of their shallow draft to anchor in locations that other boats cannot. This allows for a greater range of cruising spots, which makes the overall experience much more enjoyable and unique.
Living on a Catamaran Full-time
For many catamaran enthusiasts, the dream of living full-time on a catamaran is entirely possible. While not without challenges, there are several factors that make living aboard a catamaran an enjoyable experience:
- Spacious living areas : Catamarans generally have more living area compared to monohulls, providing ample space for the whole crew.
- Privacy : The separate hulls allow for private cabins, ensuring that everyone on board has their space.
- Stability : As mentioned earlier, catamarans are stable vessels, making living on them more comfortable than monohulls.
Choosing Your Catamaran
Comparing Models and Features
When I start to look for the perfect catamaran, the first thing I focus on is comparing various models and features .
I determine the key factors that are essential for my needs, such as size, passenger comfort, and performance. By doing so, I can identify which catamaran models are most suitable for me.
For example, if I plan to sail with a large group, I would look for a catamaran that offers ample space both inside and out.
To help me with my comparisons, I usually create a table or list of the different models and their features:
| Model | Size | Comfort | Performance |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 40ft | Spacious | High |
| B | 35ft | Average | Average |
| C | 45ft | Luxury | High |
This visual aid makes it easier for me to sort the options and prioritize my considerations, such as price, yacht type, and brand.
New vs. Second-Hand
Another critical aspect of choosing a catamaran is deciding between a new or second-hand boat.
Both options have their pros and cons, and ultimately it depends on my preferences and budget.
If I can afford a new catamaran, I get the advantage of the latest design , features, and technology. Plus, I typically receive better warranty coverage and support from the manufacturer.
However, new catamarans are more expensive and can have long wait times due to high demand.
On the other hand, purchasing a second-hand catamaran can save me a significant amount of money, and I might find a high-quality boat with low mileage or well-maintained by the previous owner.
However, this option carries more risks, as I need to be knowledgeable about potential maintenance issues and conduct a thorough inspection before purchase.
Learning Resources
Books and Manuals
When it comes to learning about catamarans, there are plenty of books and manuals available.
One of the highly recommended books is Multihull Voyaging by Thomas Firth Jones. This book provides a comprehensive understanding of multihulls, including catamarans, and is an essential guide for any beginner sailor.
Another great book to check out is Catamarans: The Complete Guide for Cruising Sailors by Gregor Tarjan.
With a foreword by Charles K. Chiodi, publisher of Multihulls Magazine, this book covers all aspects of cruising catamarans. It includes detailed information on design, construction, and maintenance, as well as tips and tricks for sailing a catamaran.
Here are a few more books that I find valuable:
- The Catamaran Book by Tim Bartlett, an excellent resource for both beginners and experienced sailors
- Catamaran Sailing: From Start to Finish by Phil Berman and Lenny Rudow, a comprehensive guide to both catamaran racing and cruising
Online Content and Photography
In addition to books, you can find plenty of online content and photography about catamarans.
Websites like Sailaway Blog and Boating Guide offer tips, techniques, and how-to articles for sailing catamarans.
Many of these sites also include stunning photography, showcasing these beautiful vessels in action.
For those who prefer Kindle or e-books, many of these resources are available in digital format.
This makes it easier for you to access them anytime, anywhere, allowing you to keep learning and improving your catamaran sailing skills.
To further enhance your knowledge, you can also join online forums and communities dedicated to catamarans.
These platforms provide invaluable advice and first-hand experiences shared by fellow sailors, as well as recommendations for additional learning resources.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors should be considered when choosing a catamaran for full-time living?
When choosing a catamaran for full-time living, consider its space and layout , as it will become your home.
Look for a design with a comfortable living area , ample storage, and sufficient berths for the number of people living aboard.
Also, consider fuel efficiency , ease of maintenance, and the catamaran's cruising range .
Lastly, the overall cost of ownership , including insurance and mooring fees, should be considered.
How do catamarans perform in rough sea conditions?
In general, catamarans are known for their stability, which is primarily due to their wide beams. This makes them less prone to capsizing when compared to monohulls.
However, their performance in rough sea conditions will depend on the specific model and design of the catamaran. Some may perform better in certain conditions than others, so researching and selecting the right design is essential.
What are the key differences between sailing a catamaran and a monohull?
One of the main differences between catamarans and monohulls is stability.
Catamarans have a wider beam , which makes them more stable and minimizes the risk of capsizing.
They also have shallower drafts, which allow them to access more shallow waters compared to monohulls.
Additionally, catamarans often have larger living spaces, making them more comfortable and suitable for cruising and full-time living.
What are the advantages of catamarans for long-distance cruising?
Catamarans offer several advantages for long-distance cruising.
Their wide, stable design provides a comfortable ride and reduces the risk of seasickness.
They can also attain higher speeds due to their reduced drag and generally sail faster than monohulls on certain points of sail.
The shallow draft allows them to explore more coastal areas and anchor closer to shore. Lastly, their spacious interiors make them ideal for extended cruises and living aboard.
How does one assess the value of a used catamaran on the market?
Assessing the value of a used catamaran requires thorough research and inspection.
Start by comparing the age, model, and condition of the catamaran to similar listings on the market.
Take note of any upgrades or additions made to the boat, as these can affect the price.
It's essential to inspect the boat in person or hire a professional surveyor to ensure there are no hidden issues that could affect its value.
What essential features should be looked for in a catamaran intended for ocean voyages?
For ocean voyages, look for a catamaran with a strong, well-built hull designed to handle rough conditions.
Safety features such as liferafts, adequate flotation, and sturdy deck hardware are crucial.
A reliable engine and well-maintained rigging and sails are also essential.
In terms of living space, opt for a catamaran with a comfortable, spacious interior and ample storage.
Last but not least, good navigation and communication systems are necessary for long-distance ocean voyages.
Related Articles

Rhodan Trolling Motor: Expert Guide to Performance and Installation

Cruising Power: Maximize Your Next Cruise Experience with Ease
How to Avoid Electrical Issues While Boating: Expert Tips and Guidelines

Lake George Florida: A Scenic Retreat for Nature Enthusiasts

Sharkbanz: The Ultimate Guide to Shark Protection Technology

INTREPID POWERBOATS AT THE 2024 PALM BEACH INTERNATIONAL BOAT SHOW

Alpha Bravo Charlie Alphabet: A Comprehensive Guide to Phonetic Codes

10-Year-Old Boy Attacked by Shark During Bahamas Resort "Walking with Sharks" Expedition

- Build Your Boat
- Tideline 235 Hybrid
- Tideline 365 Offshore
- News & Events

- Schedule a Sea Trial
A Guide to Catamarans: Exploring the Beauty of Twin-Hull Vessels

Catamarans are a fascinating class of vessels that have captured the imagination of sailors and water enthusiasts worldwide. With their distinctive twin-hull design and numerous advantages, catamarans have become increasingly popular in recent years. Whether you’re a seasoned sailor or a novice to the world of boating, this guide will introduce you to the allure of catamarans and help you navigate your way through these remarkable vessels.
Understanding Catamarans: The Basics
1. Twin-Hull Design : At the heart of every catamaran is its twin-hull design. Two parallel hulls provide stability and buoyancy. This design offers several advantages, including reduced rolling motion, increased deck space, and shallower draft, making them suitable for various water environments.
2. Stability : Catamarans are renowned for their exceptional stability. The wide-set hulls offer a solid platform, reducing the tendency to heel (tilt) in strong winds or rough seas. This stability is a key reason catamarans are favored by those who are prone to seasickness.
3. Speed and Fuel Efficiency : The dual-hull design creates less drag, allowing catamarans to achieve impressive speeds and superior fuel economy. The reduced water displacement means they can be faster and more fuel efficient than monohull vessels of the same size. This speed and fuel efficiency makes catamarans ideal for both leisure cruising and competitive racing.
4. Deck Space : Catamarans provide ample deck space, which is perfect for fishing, sunbathing, or just relaxing. The absence of a central keel and a tapered bow enables you to make the most of the deck space, often with a seamless connection between indoor and outdoor areas.
Types of Catamarans
Catamarans come in various shapes and sizes, each designed for specific purposes. Here are some common types:
1. Sailing Catamarans : These are designed primarily for sailing, offering the joy of wind-powered navigation. Sailing catamarans often have spacious living areas and are great for extended cruising.
2. Power Catamarans : Power catamarans are equipped with engines for those who prefer motor-driven propulsion. They are known for their efficiency, stability, and relatively shallow draft, making them suitable for a variety of applications, from fishing to luxury charters.
3. Cruising Catamarans : These are designed for long journeys, often with comfortable living quarters, kitchens, and spacious cabins. Cruising catamarans are popular for people looking to explore coastal and offshore destinations.
4. Racing Catamarans : These are built for speed and competitive racing. They have sleek designs, lightweight construction, and advanced rigging systems, making them the choice for adrenaline enthusiasts.
Advantages of Catamarans
1. Stability : Catamarans offer excellent stability both at anchor and underway. This stability is a key reason families and novice sailors often opt for catamarans.
2. Spacious Interiors : Catamarans provide ample living space, with multiple cabins, saloons, and kitchens. The wide beam allows for a comfortable and roomy interior.
3. Reduced Draft : Catamarans have a shallow draft, allowing them to access shallower waters, hidden coves, and secluded anchorages that might be off-limits to deeper-draft monohull boats.
4. Maneuverability : Catamarans can execute tight turns with precision, making them easier to dock and navigate in marinas.
5. Safety : Thanks to their buoyancy and stability, catamarans are less prone to capsizing, making them a safer choice, especially for families.
Challenges of Catamarans
1. Maintenance : Catamarans often have more complex systems due to their twin engines and two hulls, which can result in increased maintenance requirements.
2. Cost : Catamarans are generally more expensive than monohull boats of similar size and age.
3. Docking Space : The wider beam of catamarans can require wider slips in marinas, which may limit docking options in some locations.
Sailing the Seas in Style
Catamarans offer a unique and exciting way to explore the world’s oceans, rivers, and lakes. Their stability, speed, and spaciousness make them an excellent choice for a wide range of water-based activities, from leisurely cruising to competitive racing. Whether you’re looking for a family-friendly vessel, a luxurious yacht, or a thrilling racing machine, catamarans have something to offer every sailor and water enthusiast. So, if you’re ready to set sail in style and comfort, consider exploring the world of catamarans and discovering the beauty of twin-hull vessels.
As you embark on your journey of discovering the world of catamarans, remember that Tideline Fishing Catamarans stands out as a shining example of excellence in this industry. With their dedication to crafting high-performance, quality vessels that seamlessly blend classic aesthetics with modern innovation, Tideline has redefined the fishing experience for anglers worldwide. If you’re intrigued by the idea of a fishing catamaran that offers exceptional comfort and seaworthiness, check out our website to explore a range of customizable models. The horizon awaits, and with Tideline Boats, your adventure is bound to be unforgettable.

Port Of Liverpool Welcomes The UK’s Largest Whole Maize Vessel

NYK & Oono Development Partner To Commercialize Ship Recycling In Japan

Watch: U.S. Coast Guard Releases First Public Video Of Titan Submersible Wreckage

Baltic Sea’s First Green Freight Corridor Reduces Transport Emissions By 90%

What are Triple Hull Vessels?
Monohull vessels have been and will be synonymous with ships, come what may. This is owing to all kinds of reasons ranging from convenience to simplicity, low costs to large capacity, ease in construction to acceptability. However, over the years, there has been an escalated demand to explore unconventional design types in the quest for advancement.

Monohull vessels, despite all kinds of efficient designs, still lacked in terms of high speed and resistance to rough sea states. Moreover, depending on their design, the basis for monohull vessels is directly related to the buoyancy factor, which essentially means that for greater size and capacity, you have to increase the displacement. Furthermore, with all monohulls, there is always some calculated risk or problems in terms of seakeeping and stability characteristics, even if in very minimal degrees for a very safe design.
The concept of multihull vessels came in response to mitigate such challenges and delve deeper into the realm of unconventional designs for improved utility. Multi-hull vessels are vessels that are characterised by the construction of multiple hulls, either two or three, known as catamarans and trimarans , respectively. The advent and application of multi-hull vessels have been the collective result of three major requirements: i) speed, ii) stability and ii) capacity.
Catamarans or twin-hull configuration was the immediate result. This configuration accommodated two hulls, mostly symmetrical and identical, connected mostly by the main deck or some crucial structural member. In almost every vessel, the superstructure or deckhouse was mounted atop the main deck.

The advent of multihulls was incongruous with the evolution of high-speed planning crafts , which used the interesting concept of hydrodynamic planning effect and partial displacement to tread through waters at high speeds and increased propulsive efficiency. Combining both these developments was quite a game-changer where small to average-sized crafts for defence or passenger flourished dramatically. These high-speed craft had planing characteristics and were hydrodynamically manifold efficient. Moreover, they catered to the requirement of higher payload and capacity over a lesser displacement.

This lesser displacement required per unit payload coupled with high-speed planing characteristics and propulsive efficacy also significantly reduced resistance, both wave-making as well as frictional (due to lesser wetted surface area from each hull).
However, along with the many advantages, some disadvantages were there still. One of them was the high degree of stress that occurred in the way of the connecting cross deck, especially in rough sea conditions. These were mostly due to the torsional and transverse behaviour exhibited as a result of two hulls tending to behave independently. Moreover, these twin-hull configurations also exhibited high motions, including effects like slamming and pounding.
Also, the problem of hydrodynamic resistance was not mitigated at low speeds. The problem of fatigue was also quite significant in the way of the cross deck, especially when the separation between the two demi-hulls was above a certain limit.
Nevertheless, catamarans, or twin-hull configurations, have been common for the last several decades, and their numbers are increasing. Some years down the line, trimarans were proposed to further streamline this problem. Trimarans are those vessels which essentially have a three-hull configuration.
These three hulls are connected by a single deck known as the cross-deck. For all practical purposes, there is a bigger main hull in the middle, and is, in turn, supported by two smaller side hulls, known as outriggers. However, some designs also have the hulls the same size as in the case of catamarans.
The main design philosophy of trimarans is nothing much different from the broad concept of multi-hull vessels: higher payload or tonnage capacity to displacement ratio. This essentially means that they are able to cater to higher carrying- capacity both in terms of weight as well as space-volume without a significant increase in the displacement that is required. This is a win-win situation for any kind of design as you are able to optimise everything that is ever ideally envisaged:
- Hydrodynamic performance
- Stability and seakeeping characteristics
- Greater deck area
- Resistance and propulsion characteristics
- Lesser required displacement
- Lesser fuel consumption
- Optimised distribution of loads and stresses
Design Philosophy of Trimarans
Trimarans were conceived based on the following design goals in mind that would ratify the reliability expectations from multihull vessels even further.
- Managing the resistance even more, especially those stemming from low speeds and large ship motions, and further improving on the speed characteristics. The powering requirements also increase dramatically.
- Reduce wetted surface area even further at similar displacements. This essentially means at even smaller displacements, the payload, as well as the available spaces and deck area, is increased. Hence, by making each of the hulls even more slender, a high value of payload can be maintained. This, in turn, even further improves on the resistance and propulsive characteristics.
- The stability of the vessel is related to the previous point. A triple hull configuration caters for higher stability, as obvious. Hence, not only are we increasing the payload but also having the upper hand on stability while improving the resistance in tandem.

Consequently, the seakeeping characteristics of the vessel are also augmented, especially during rough sea states.
- Flexibility in terms of design. When there is an availability of more space and deck areas, there is more amount of freedom to augment the arrangement.
- Structural strength. This is one of the most crucial aspects associated with the design of trimarans. A 3-hull configuration increases the structural strength of the vessel manifold, both in terms of transverse and longitudinal.
- All oncoming loads on the vessel are distributed more efficiently on the three hulls. As a result, the strength-bearing capacity of the vessel under all circumstances of sea states and motions of the vessel is improved. This also compensates in terms of increased higher usable payload even further. Safety and reliability also come hand-in-hand with strength. Henceforth, a greater strength translates to higher survivability.
Lastly, due to the above advantages, the reduced cost of the vessel in terms of lower material requirements as lighter structural weight can be commensurate to a better design.
Though mostly similar to conventional vessels, the initial design process of trimarans involves the following important aspects:
- Deciding on the stability parameters like metacentric height . As the vessel is already inherently stable, GM height can be increased. Moreover, as per regulations, if the main deck height (and hence the above-water clearance) of the cross-deck(s), which is related to the GM itself, is more than 5% of the waterline length of the vessel, motions like slamming decrease significantly. Hence, trimarans offer much more freedom to increase the GM as compared to conventional vessels.
- Deciding the dimensions of the side hulls. This is also closely related to the damage stability criteria.
- Designing the cross-deck is important, just like in the case of catamarans. The adequate stiffening of the same is also crucial.
- Separation between the hulls based on resistance, strength and utility of the vessel.
- Finally, meticulous allocation of the internal spaces optimising the design and the requirement.
However, multi-hull vessels become less feasible as vessel sizes increase due to a wide range of factors like lack of planing characteristics, lesser feasibility in design, complexity in construction, and so on. Nevertheless, many designs, especially within the gamut of defence vessels, passenger vessels, and other special types of vessels , have explored the feasibility of multi-hull designs with evolution over the years. They have been important successes, even if at a higher cost.
You might also like to read-
- Types of Hulls Used For Vessels
- Different Parts Of A Ship’s Hull
- What is a Skeg in a Vessel?
- Understanding Vessel’s Hull Speed And Its Determination
- Understanding Hunting Gear Mechanism Of Ships
- Understanding The Beam Of A Ship

Safer ships, Cleaner Oceans – Hull Protection Systems – Vol 13
- Introduced based on the fact that there is a changing trend in the way books are read today.
- For marine engineers
- Pay by Credit Card/Debit Card/Net Banking
- Read Instantly
- Guaranteed For 30 Days
Disclaimer : The information contained in this website is for general information purposes only. While we endeavour to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability or availability with respect to the website or the information, products, services, or related graphics contained on the website for any purpose. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
In no event will we be liable for any loss or damage including without limitation, indirect or consequential loss or damage, or any loss or damage whatsoever arising from loss of data or profits arising out of, or in connection with, the use of this website.

About Author
Subhodeep is a Naval Architecture and Ocean Engineering graduate. Interested in the intricacies of marine structures and goal-based design aspects, he is dedicated to sharing and propagation of common technical knowledge within this sector, which, at this very moment, requires a turnabout to flourish back to its old glory.
Read More Articles By This Author >

Do you have info to share with us ? Suggest a correction
Daily Maritime News, Straight To Your Inbox
Sign Up To Get Daily Newsletters
Join over 60k+ people who read our daily newsletters
By subscribing, you agree to our Privacy Policy and may receive occasional deal communications; you can unsubscribe anytime.

BE THE FIRST TO COMMENT
Leave a reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Subscribe to Marine Insight Daily Newsletter
" * " indicates required fields
Marine Engineering
Marine Engine Air Compressor Marine Boiler Oily Water Separator Marine Electrical Ship Generator Ship Stabilizer
Nautical Science
Mooring Bridge Watchkeeping Ship Manoeuvring Nautical Charts Anchoring Nautical Equipment Shipboard Guidelines
Explore
Free Maritime eBooks Premium Maritime eBooks Marine Safety Financial Planning Marine Careers Maritime Law Ship Dry Dock
Shipping News Maritime Reports Videos Maritime Piracy Offshore Safety Of Life At Sea (SOLAS) MARPOL
WAIT! Did You Download 13 FREE Maritime eBooks?
Sign-up and download instantly!
We respect your privacy and take protecting it very seriously. No spam!

Catamaran Hulls- Everything You Need To Know
- Post Written By: Boater Jer
- Published: July 17, 2022
- Updated: July 19, 2022

Disclaimer: You might notice that we recommend products in some articles. We may earn a commission for referring you if you click the link and buy a product.
We only recommend products we’ve tried/tested/own (that’s why you won’t find thousands of affiliate links on my site). If you have experience with one of the products we’ve mentioned, please share your experiences in the comments at the end.
Catamaran hulls are not like normal boats but provide increased stability. Let’s take a look at these incredible boats and how their hulls create one of the most versatile watercraft available today.
The Tamil Cholas used catamarans to ferry their troops to invade Malaysia, Indonesia, and Burma. The early paravars or fishing communities in the southern part of Tamil Nadu used two-hulled boats to fish. Polynesian seafarers were also early users of the catamaran, utilizing the watercraft to get to hard-to-reach islands. ( source )
Although the catamaran hull concept is a relatively new introduction to modern boat design , the boat has been in use since the 5th century. It was used for fishing, traveling, and transporting people and supplies.
Parts Of A Catamaran
Here are the basic parts of the modern sailing catamaran:
- Hulls are what sets this boat apart from the rest. The catamaran has two hulls, while the monohull, as the name suggests, has only one hull. Most of the advantages of this boat are hinged on these two hulls.
- The bridge deck connects the two catamaran hulls.
- On top of the catamaran hulls and the bridge deck is the deck . It is where owners attach most of the equipment in a boat.
- You can locate the berth, the galley, and other living amenities in the cabin .
- The cockpit is where you find the navigation equipment of the boat . It is where you control the catamaran’s rudder, sails, and engine.
Types Of Catamaran

The modern catamaran is far more different than its crude ancestor. Instead of tree cutouts, catamarans are now carbon fiber or fiberglass. Here are the different types of catamarans:
Based On function
Pontoons are usually present on rivers and lakes and sometimes even on oceans, but they only travel near the shore.
In a catamaran pontoon-type boat, the pontoons serve as storage areas, where you will find the onboard motors. They are useful for water leisure activities such as short water trips, tubing, wakeboarding, and water skiing.
Some pontoons may also serve as houseboats. They provide a broader, more stable platform ideal for a floating house. Plus, the space is bigger, and most of it is above water. It offers a better viewing option than a monohull. ( Source )
Small Waterplane Area Twin Hull is a catamaran-type boat that the United States Navy initially used for military purposes. They provide the water stability that is necessary when transporting heavy military equipment.
One example of a military SWATH catamaran is the Spearhead class EPF. It is as long as a World War II escort destroyer, yet it is twice as fast at 43 knots. It can reach that speed because of its two separate hulls.
Because of their innate speed, SWATH catamarans can become patrol boats in lakes and rivers. They can easily outrun and outmaneuver standard watercraft.
Nowadays, there are SWATH cruise ships and other non-military variations. ( Source )
Based On Design
- Sailing Catamaran
The smaller sailing catamarans do not have auxiliary engines, so the owner can propel the boat by harnessing the wind using the sails. It’s a popular choice for people with very little or no sailing experience because they are light and easy to use.
The larger sailing catamarans are for group charters and long-distance cruising. They have become so popular lately that they now outnumber monohulls in tropical locations all over the world. They have a last, a headsail, and a mainsail. And the twin hulls have one engine each.
- Power Catamaran
Unlike their sailing cousins, the powered catamarans do not have sails. They have massive engines which provide high speed. Their twin hulls are stronger and can carry and protect the large motors.
The smaller “powercats” are used mainly for fishing. The bigger ones are rented out for charters and cruises.
Catamaran Hulls Performance
Thanks to the catamaran hulls, the boat offers many advantages over other boat types.
- Because its dual-hull design provides a broader base, it offers more water stability than monohull boats. It makes the cat (catamaran) a popular choice for fishing expeditions and cruises.
- Riding a catamaran is ideal for people who feel seasick whenever they ride boats. The twin hulls prevent the boat from moving from side to side. The hulls allow the boat to travel smoothly, even on moderately choppy waters.
- The catamaran is the best choice when storing provisions and other household items with less heeling and bobbing.
- The twin hulls’ stability is ideal for many activities such as cooking and partying.
- Cats offer more moving space because of their broader base, thanks to dual hulls.
- With a catamaran, you have two great options on where to hang out. You can do it on the spacious deck or below the galley.
- Compared to a monohull of the same size, the catamaran can accommodate more equipment and people.
- The living area in a catamaran is above the water line. This feature provides more natural light, a greater view of the outside, and better air circulation.
- Since catamarans do not have keels, they can anchor on shallow waters, something that most monohulls will not be able to do. This ability of catamaran boats is impressive, especially if you are going around areas with many reefs and small islands.
- Catamaran hulls allow the boat to cut through the waves easier and faster. It means they require less engine power than their monohull counterparts.
- Because it has two engines and two rudders, the catamaran can easily maneuver in very tight spaces.
- Because they do not carry heavy keels, catamarans can sail faster than monohulls.
- The catamaran’s stability, speed, and weight make it a safer option than the monohull. It can sail in shallow waters, make a 360 degrees maneuver effortlessly, and carry more provisions.
Disadvantages Of A Catamaran
Like any other boat type, the catamaran also has drawbacks and limitations. Here are some of them:
- The catamaran hulls prevent the boat from sailing as fast as the monohull upwind. The two hulls cause drag, and this slows the boat considerably.
- Because of its bigger size, looking for a docking site can be more difficult and costlier than a monohull.
- For hardcore sailing fans, the experience of sailing with a catamaran will never be able to match that of sailing with a monohull. To them, the challenge of true sailing is just not there with a catamaran.
What Are The Hulls Of The Catamaran Called?
According to the Online Etymology Dictionary, the Tamil word கட்டுமரம், which is pronounced as kattumaran, is where the word catamaran takes its name. The word means “pieces of logs tied together”. Through the years, the term has evolved into what is now a catamaran in English.
What Are The Characteristics Of A Catamaran Hull?
- Both hulls of a catamaran complement each other to achieve very minimum water resistance.
- Because of this, it takes less energy to propel a catamaran, whether via an engine or sails.
- The catamaran hulls provide stability to the boat. The twin-hull significantly reduces bobbing.
- The catamaran’s ability to keep steady on the water makes it an ideal vessel for cooking, dining, and storing provisions.
Are Catamarans Good In Rough Water?
Catamarans are amazingly stable in rough water. The catamaran’s design and build, which provides stability, are factors why it is one of the best boats to use when the waters are choppy.
Yes, catamarans are relatively more expensive than monohulls. Nevertheless, since single-hull boats are less expensive, their resale value is also cheap.
If you add all the advantages that a catamaran offers – safety, comfort, and speed- it does not come out expensive.
patekphilippe.io
Share this post with your friends, subscribe to our newsletter.
Join us in our love for all things water. And Adventure.

4 Common Types Of Propulsion For Boats
Boats seem simple, they float and move you’re across the water, right? Well, it can be just a little more complicated than just that. Let’s take a look at those 4 common types Of propulsion for boats. I’ll review the Pros and Cons for each type to give you a good idea about each.

A Guide To Lake Fishing On A Boat
There’s nothing quite as peaceful as being out on the water on a cool summer morning. Going out lake fishing on a boat, watching the mist rise up from the glass-like water is such a joy. The tranquility as the sun slowly peaks up from the horizon is both calming and awe-inspiring.

Do Flat Bottom Boats Have Titles?
Have you ever wondered if Flat Bottom Boats have titles? It’s a perfectly valid question, and essential to know if you plan on purchasing a flat bottom boat or already own one. Or maybe you have a different kind of boat and are wondering about the need for a title? A title is a document

Can You Wakeboard Behind A Bass Boat?
Can you wakeboard behind a bass boat? Find all the answers here from wakeboard requirements to bass boat abilities.

How Long Does It Take A Canoe To Go… (Canoe Calculator Here)
You asked, and we answered: Here’s a calculator to determine how long your canoe trip will take. The calculator uses the average speed of an average canoe in calm water. Here it is: The Canoe Trip Time Calculator: Canoe Trip Calculator Enter the distance: Kilometers Miles Calculate Canoe Articles & Information replica rolex

Pontoon Boat Basics
Heading out to the lake? Well, there’s no better way to enjoy the day than from your pontoon boat. Imagine the fun you’ll have with family and friends cruising around in the sunshine. Even if you’re a novice, a pontoon boat is easy enough to maneuver.

Boat Information By Type
© 2023 Boating.Guide, A Hyperwave Media Group Ltd. Publication.
Privacy Overview
Did You Know That We Offer Contract to Closing Services? Click Here to Find Out More.
Need Marine Financing? Apply Here With Our Partner, First Approval Source
- Catamaran Interviews
- Catamaran Reviews
- Buying Advice
- Selling Advice
- Woods Design Advice
- Admiral 38
- Admiral 40
- Admiral 50
- Americat 3014
- Antares 44
- Aquila 44
- Aquila 48 Power Catamaran
- Aventura 37
- Balance 442
- Balance 482
- Balance 526
- Bali 4.0
- Bali 4.1
- Bali 4.2
- Bali 4.3
- Bali 4.4
- Bali 4.5
- Bali 4.6
- Bali 4.8
- Bali 40 Catspace
- Bali 5.4
- Bali Catsmart
- Beneteau Blue II
- Broadblue 346
- Broadblue 38 Prestige
- Broadblue 385
- Broadblue 435
- Broadblue 46
- Rapier 400
- Rapier 550
- Catalac 10M
- Catalac 11M
- Catalac 12M
- Catalac 8M
- Catalac 900
- Catalac 9M
- Catana 381
- Catana 39
- Catana 401
- Catana 40S
- Catana 411
- Catana 42
- Catana 42 S
- Catana 431
- Catana 44
- Catana 471
- Catana 50
- Catana 521
- Catana 531
- Catana 55
- Catana 581
- Catana 65
- Catathai 44
- Chris White
- Chris White 48 Voyager
- Chris White 55
- Condor 40
- Contour 34
- Corsair F28 R
- De Villiers
- Dean 365
- Dean 400
- Dean 440
- Dean 500
- Dix DH550
- Dolphin 380
- Dolphin 460
- Edel 35
- Endeavour 30
- Endeavour 35 Victory
- Endeavour 36
- Endeavour 44
- Endeavour 44 TrawlerCat
- Endeavour 50 Pilothouse Trawler
- Excess 11
- Excess 15
- F-41
- Fastback 43
- Fastcat 445
- Fisher 28
- Fisher 32
- Fortuna 36 Island Spirit
- Fortuna 401 Island Spirit
- Fountaine Pajot
- FP 32 Maldives
- FP 35 Tobago
- FP 36 Mahe
- FP 37 Antigua
- FP 38 Athena
- FP 39 Fidji
- FP 40 Isla
- FP 40 Lavezzi
- FP 40 Lucia
- FP 40 MY
- FP 40 Summerland MY
- FP 41 Lipari
- FP 42 Astrea
- FP 42 Venezia
- FP 43 Belize
- FP 44 Helia
- FP 44 Orana
- FP 45 Elba
- FP 46 Bahia
- FP 46 Casamance
- FP 48 Salina
- FP 50 Saba
- FP 56 Marquises
- FP 57 Sanya
- FP 58 Ipanema
- FP 60 Eleuthera
- FP Saona 47
- Fusion 40
- Gemini 105
- Gemini 3000
- Gemini 3200
- Gemini 3400
- Gemini Freestyle 37
- Gemini Freestyle 399 Power
- Gemini Legacy 35
- Grainger 420 Mystery Cove
- Gunboat 55
- Hirondelle 7M
- HopYacht 30
- Island Packet
- Island Packet Cat 35
- Kennex 420
- Knysna 440
- Knysna 480
- Knysna 500
- Knysna 550
- Lagoon 35
- Lagoon 37 TPI
- Lagoon 380
- Lagoon 39
- Lagoon 40
- Lagoon 400
- Lagoon 410
- Lagoon 42
- Lagoon 42 TPI
- Lagoon 420
- Lagoon 421
- Lagoon 43 PC
- Lagoon 44 Power Cat
- Lagoon 440
- Lagoon 450
- Lagoon 46
- Lagoon 470
- Lagoon 50
- Lagoon 500
- Lagoon 52F
- Lagoon 55
- Lagoon 560
- Lagoon 570
- Lagoon 620
- Lagoon Seventy 8
- Lagoon Sixty 7
- Leeuwin 42
- Leopard 38
- Leopard 39
- Leopard 39 PowerCat
- Leopard 40
- Leopard 42
- Leopard 43
- Leopard 44
- Leopard 45
- Leopard 45 Classic
- Leopard 46
- Leopard 46 Lion PowerCat
- Leopard 47
- Leopard 47 PowerCat
- Leopard 48
- Leopard 50
- Leopard 51 PowerCat
- Leopard 53 PowerCat
- Leopard 58
- Lidgard 73 Executive
- Looping 50
- Maine Cat 30
- Maine Cat 38
- Maine Cat 41
- Manta 40
- Manta 42
- Matrix 450 Vision
- Matrix 760 Silhouette
- Maverick 400
- Maverick 420
- Maverick 440
- Moxie 61
- Nautitech 40
- Nautitech 40 Open
- Nautitech 44 Open
- Nautitech 442
- Nautitech 46 Open
- Nautitech 47
- Nautitech 47 Power
- Nautitech 475
- Nautitech 65
- Neel 45
- Neel 47
- Outremer 40
- Outremer 45
- Outremer 50 Standard
- Outremer 55
- Outremer 5X
- PDQ 32
- PDQ 36
- PDQ 42 Antares
- Privilege 37
- Privilege 39
- Privilege 42
- Privilege 43
- Privilege 435
- Privilege 45
- Privilege 465
- Privilege 48 Transcat
- Privilege 482
- Privilege 495
- Privilege 510
- Privilege 65
- Privilege Serie 5
- Prout 31 Quest
- Prout 33 Quest
- Prout 34 Event
- Prout 35 Snowgoose
- Prout 37 Snowgoose
- Prout 37 Snowgoose Elite
- Prout 38
- Prout 38 Manta
- Prout 39 Escale
- Prout 45
- Prout 46
- Royal Cape 45
- Royal Cape 500 Majestic
- Royal Cape 530 Majestic
- Sailcraft 30 Iroquois
- Sailcraft 32 Comanche
- Sailcraft 35 Cherokee
- Sailcraft 41 Apache
- Sailcraft 44 Apache
- Scape 39
- Wildcat 350
- Seacart 30
- Seawind 1000
- Seawind 1160
- Seawind 1190
- Seawind 1200
- Seawind 1260
- Seawind 1600
- Simpson 48
- Solaris 36 Sunrise
- Solaris 36 Sunstar
- Solaris 42
- St Francis 44
- St Francis 48
- St Francis 50
- Stealth 11.8
- Sunreef 60
- Sunreef 62
- Sunreef 70
- Sunreef 74C
- Sunreef 82 DD
- Sunreef 88 DD
- Switch 51
- Switch 55
- TRT 1200
- Heavenly Twins 26
- Ocean Twins 38
- Vaan R5
- Vision 444
- Voyage 380 Maxim
- Voyage 400 Norseman
- Voyage 430 Norseman
- Voyage 440
- Voyage 450 Cabriolet
- Voyage 47 Mayotte
- Voyage 480
- Voyage 500
- Voyage 580
- Voyage 590
- Kronos 45
- Wharram 38 Tiki
- AMI 320 Renaissance
- Woods 22 Wizard
- Woods 35 Banshee
- Woods 35 Flica
- Woods 36 Scylla
- Woods 36 Vardo
- Woods 38 Transit
- Woods 40 Meander
- Xquisite X5
- Xquisite X5+
Catamaran Design Formulas
- Post author By Rick
- Post date June 29, 2010
- 10 Comments on Catamaran Design Formulas

Part 2: W ith permission from Terho Halme – Naval Architect
While Part 1 showcased design comments from Richard Woods , this second webpage on catamaran design is from a paper on “How to dimension a sailing catamaran”, written by the Finnish boat designer, Terho Halme. I found his paper easy to follow and all the Catamaran hull design equations were in one place. Terho was kind enough to grant permission to reproduce his work here.
Below are basic equations and parameters of catamaran design, courtesy of Terho Halme. There are also a few references from ISO boat standards. The first step of catamaran design is to decide the length of the boat and her purpose. Then we’ll try to optimize other dimensions, to give her decent performance. All dimensions on this page are metric, linear dimensions are in meters (m), areas are in square meters (m2), displacement volumes in cubic meters (m3), masses (displacement, weight) are in kilograms (kg), forces in Newton’s (N), powers in kilowatts (kW) and speeds in knots.
Please see our catamarans for sale by owner page if you are looking for great deals on affordable catamarans sold directly by their owners.
Length, Draft and Beam
There are two major dimensions of a boat hull: The length of the hull L H and length of waterline L WL . The following consist of arbitrary values to illustrate a calculated example.
L H = 12.20 L WL = 12.00

After deciding how big a boat we want we next enter the length/beam ratio of each hull, L BR . Heavy boats have low value and light racers high value. L BR below “8” leads to increased wave making and this should be avoided. Lower values increase loading capacity. Normal L BR for a cruiser is somewhere between 9 and 12. L BR has a definitive effect on boat displacement estimate.
| B L / L | In this example L = 11.0 and beam waterline B will be: |
| Figure 2 | |
| B = 1.09 | A narrow beam, of under 1 meter, will be impractical in designing accommodations in a hull. |
| B = B / T | A value near 2 minimizes friction resistance and slightly lower values minimize wave making. Reasonable values are from 1.5 to 2.8. Higher values increase load capacity. The deep-V bottomed boats have typically B between 1.1 and 1.4. B has also effect on boat displacement estimation. |
| T = B / B T = 0.57 | Here we put B = 1.9 to minimize boat resistance (for her size) and get the draft calculation for a canoe body T (Figure 1). |
| Midship coefficient – C | |
| C = A / T (x) B | We need to estimate a few coefficients of the canoe body. where A is the maximum cross section area of the hull (Figure 3). C depends on the shape of the midship section: a deep-V-section has C = 0.5 while an ellipse section has C = 0.785. Midship coefficient has a linear relation to displacement. In this example we use ellipse hull shape to minimize wetted surface, so C = 0.785 |
| Figure 3 |
| C =D / A × L | where D is the displacement volume (m ) of the boat. Prismatic coefficient has an influence on boat resistance. C is typically between 0.55 and 0.64. Lower values (< 0.57) are optimized to displacement speeds, and higher values (>0.60) to speeds over the hull speed (hull speed ). In this example we are seeking for an all round performance cat and set C := 0.59 |
| C = A / B × L | where A is water plane (horizontal) area. Typical value for water plane coefficient is C = 0.69 – 0.72. In our example C = 0.71 |
| m = 2 × B x L × T × C × C × 1025 m = 7136 | At last we can do our displacement estimation. In the next formula, 2 is for two hulls and 1025 is the density of sea water (kg/m3). Loaded displacement mass in kg’s |
| L = 6.3 | L near five, the catamaran is a heavy one and made from solid laminate. Near six, the catamaran has a modern sandwich construction. In a performance cruiser L is usually between 6.0 and 7.0. Higher values than seven are reserved for big racers and super high tech beasts. Use 6.0 to 6.5 as a target for L in a glass-sandwich built cruising catamaran. To adjust L and fully loaded displacement m , change the length/beam ratio of hull, L . |
| m = 0.7 × m m = 4995 | We can now estimate our empty boat displacement (kg): This value must be checked after weight calculation or prototype building of the boat. |
| m = 0.8 × m m = 5709 | The light loaded displacement mass (kg); this is the mass we will use in stability and performance prediction: |
| The beam of a sailing catamaran is a fundamental thing. Make it too narrow, and she can’t carry sails enough to be a decent sailboat. Make it too wide and you end up pitch-poling with too much sails on. The commonly accepted way is to design longitudinal and transversal metacenter heights equal. Here we use the height from buoyancy to metacenter (commonly named B ). The beam between hull centers is named B (Figure 4) and remember that the overall length of the hull is L . | |
| Figure 4 |
| Length/beam ratio of the catamaran – L | |
| L = L / B | If we set L = 2.2 , the longitudinal and transversal stability will come very near to the same value. You can design a sailing catamaran wider or narrower, if you like. Wider construction makes her heavier, narrower means that she carries less sail. |
| B = L / L B = 5.55 | Beam between hull centers (m) – B |
| BM = 2[(B × L x C / 12) +( L × B × C x (0.5B ) )] × (1025 / m ) BM = 20.7 | Transversal height from the center of buoyancy to metacenter, BM can be estimated |
BM = (2 × 0.92 x L × B x C ) / 12 x (1025 / m ) BM = 20.9 | Longitudinal height from the center of buoyancy to metacenter, BM can be estimated. Too low value of BM (well under 10) will make her sensitive to hobby-horsing |
| B = 1.4 × B | We still need to determine the beam of one hull B (Figure 4). If the hulls are asymmetric above waterline this is a sum of outer hull halves. B must be bigger than B of the hull. We’ll put here in our example: |
| B = B B B = 7.07 | Now we can calculate the beam of our catamaran B (Figure 4): |
| Z = 0.06 × L Z = 0.72 | Minimum wet deck clearance at fully loaded condition is defined here to be 6 % of L : |
| EU Size factor | |
| SF=1.75 x m SF = 82 x 10 | While the length/beam ratio of catamaran, L is between 2.2 and 3.2, a catamaran can be certified to A category if SF > 40 000 and to B category if SF > 15 000. |
| Engine Power Requirements | |
| P = 4 x (m /1025)P = 28 | The engine power needed for the catamaran is typically 4 kW/tonne and the motoring speed is near the hull speed. Installed power total in Kw |
| V = 2.44 V = 8.5 | Motoring speed (knots) |
| Vol = 1.2(R / V )(con x P ) Vol = 356 | motoring range in nautical miles R = 600, A diesel engine consume on half throttle approximately: con := 0.15 kg/kWh. The fuel tank of diesel with 20% of reserve is then |
- Tags Buying Advice , Catamaran Designers

Owner of a Catalac 8M and Catamaransite webmaster.
10 replies on “Catamaran Design Formulas”
Im working though these formuals to help in the conversion of a cat from diesel to electric. Range, Speed, effect of extra weight on the boat….. Im having a bit of trouble with the B_TR. First off what is it? You don’t call it out as to what it is anywhere that i could find. Second its listed as B TR = B WL / T c but then directly after that you have T c = B WL / B TR. these two equasion are circular….
Yes, I noted the same thing. I guess that TR means resistance.
I am new here and very intetested to continue the discussion! I believe that TR had to be looked at as in Btr (small letter = underscore). B = beam, t= draft and r (I believe) = ratio! As in Lbr, here it is Btr = Beam to draft ratio! This goes along with the further elaboration on the subject! Let me know if I am wrong! Regards PETER
I posted the author’s contact info. You have to contact him as he’s not going to answer here. – Rick
Thank you these formulas as I am planning a catamaran hull/ house boat. The planned length will be about thirty six ft. In length. This will help me in this new venture.
You have to ask the author. His link was above. https://www.facebook.com/terho.halme
I understood everything, accept nothing makes sense from Cm=Am/Tc*Bwl. Almost all equations from here on after is basically the answer to the dividend being divided into itself, which gives a constant answer of “1”. What am I missing? I contacted the original author on Facebook, but due to Facebook regulations, he’s bound never to receive it.
Hi Brian, B WL is the maximum hull breadth at the waterline and Tc is the maximum draft.
The equation B TW = B WL/Tc can be rearranged by multiplying both sides of the equation by Tc:
B TW * Tc = Tc * B WL / Tc
On the right hand side the Tc on the top is divided by the Tc on the bottom so the equal 1 and can both be crossed out.
Then divide both sides by B TW:
Cross out that B TW when it is on the top and the bottom and you get the new equation:
Tc = B WL/ B TW
Thank you all for this very useful article
Parfait j aimerais participer à une formation en ligne (perfect I would like to participate in an online training)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Crossword Solver found 30 answers to "three hulled catamaran", 8 letters crossword clue. The Crossword Solver finds answers to classic crosswords and cryptic crossword puzzles. Enter the length or pattern for better results. Click the answer to find similar crossword clues . A clue is required.
Power-power-catamaran. Power Catamaran. Power-rigid-inflatable-boats-(rib) Rigid Inflatable Boats (RIB) Power-runabout. Runabout. ... On average, they have a sail area of 936 square feet, but some yachts go as high as 2,131 square feet. Listed hull types include trimaran. Manufactured by a variety of yacht building companies, there are ...
It also has more room than a 43-foot monohull and offers single level living that doesn't leave you buried down in a dark hull. The NEEL 43 is all about out-of-the-box thinking that just may make you ponder life on three hulls. Specifications: LOA: 43' 0". Beam: 24' 7". Draft: 5'0". Displacement: 19,850 lbs.
Builder: leopard catamarans.co.uk. Bali 4.2. This French yard set a standard by which all multihulls have subsequently been judged when it launched the Bali 4.3 Loft. It blends indoor and outdoor areas into a single vast space that can be closed off with the garage door-style aft bulkhead.
Large cruising catamarans (40ft now counts as a small one) are a world apart from monohull sailing, but there's a sub-tribe of sailors dedicated to life on three hulls and builders such as Dragonfly, Corsair, Farrier, and Astus give them plenty of choice. ... Much of the advice will apply to all multihulls, whether two or three-hulled, while ...
Take a closer look at world's best catamaran and trimaran multihull yachts, including a Game of Thrones-inspired support vessel and the world's largest trimaran. ... The twin hulled 88.15 metre yacht is based on the proa design that has been used for more than 2,000 years to build fishing boats in the Pacific region. Her stability was put to ...
Bruneel argues that one prop pushing one hull is more efficient than typical catamaran set-ups and says the 75hp saildrive propels her at a cruising speed of 9 knots.
The result is telling on the water, as it should be for any best catamaran contender, where you can log easy miles: we clocked late 7s upwind, reached in the late 8s and regularly averaged 9 knots ...
Listed hull types include catamaran, trimaran, monohull and other. Built by a wide variety of yacht builders, there are currently 1,246 multi-hull yachts for sale on YachtWorld, with 268 new vessels for sale, and 978 used and custom yachts listed. These vessels are all listed by professional yacht brokers and new boat dealers, mainly in the ...
Trimarans are a unique type of sailboat, with three hulls instead of the more common two-hulled design. The three hulls on a trimaran are typically connected by a central frame, and are made of lightweight yet durable materials such as fiberglass or aluminum. This allows for a lighter and more maneuverable sailing experience.
Catamaran Sailing Techniques Part 3: Anchoring and picking up a mooring - with Nigel Irens ... Three hulls better than two - how the Neel 51 trimaran is challenging its many twin-hulled ...
Speed and Efficiency. Power catamarans have gained popularity for offering a unique combination of speed, efficiency, and stability. Their dual-hull design allows for less water resistance, which directly translates to higher speeds and better fuel efficiency compared to traditional monohull boats.. In addition, the wide beam provided by the two hulls ensures a stable ride even at higher speeds.
Multi-Hull sailing vessels pricing. Multi-Hull sailing vessels for sale on YachtWorld are available across a broad price range from £27,900 on the relatively more affordable end up to £4,775,079 for the most unique, bespoke yachts. Find Multi-hull boats for sale in your area & across the world on YachtWorld. Offering the best selection of ...
The word "catamaran" is derived from the Tamil word, kattumaram (கட்டுமரம்), which means "logs bound together" and is a type of single-hulled raft made of three to seven tree trunks lashed together. The term has evolved in English usage to refer to unrelated twin-hulled vessels. [2] [3] [4]
Multihull. The relationship between monohulls & multihulls. A multihull is a boat or ship with more than one hull, whereas a vessel with a single hull is a monohull. The most common multihulls are catamarans (with two hulls), and trimarans (with three hulls). There are other types, with four or more hulls, but such examples are very rare and ...
Understanding Catamarans: The Basics. 1. Twin-Hull Design: At the heart of every catamaran is its twin-hull design. Two parallel hulls provide stability and buoyancy. This design offers several advantages, including reduced rolling motion, increased deck space, and shallower draft, making them suitable for various water environments. 2.
Catamarans or twin-hull configuration was the immediate result. This configuration accommodated two hulls, mostly symmetrical and identical, connected mostly by the main deck or some crucial structural member. ... This is one of the most crucial aspects associated with the design of trimarans. A 3-hull configuration increases the structural ...
The Best Catamarans for Sailing Around the World A catamaran is a double-hulled boat with a deck or cabin area in between (bluewater cat definition in this article).The double hull design means that the boat rocks less, sits higher on the water, uses less fuel to sail, and can be sailed in shallower waters than a single-hulled boat without worrying about grounding.
Listed hull types include catamaran, monohull, trimaran, deep vee and other. Built by a wide variety of yacht building companies, YachtWorld presently offers a selection of 1,963 catamaran yachts for sale. Among them, 486 are newly built vessels available for purchase, while the remaining 1,477 comprise used and custom yachts listed for sale.
Parts Of A Catamaran. Here are the basic parts of the modern sailing catamaran: Hulls are what sets this boat apart from the rest. The catamaran has two hulls, while the monohull, as the name suggests, has only one hull. Most of the advantages of this boat are hinged on these two hulls. The bridge deck connects the two catamaran hulls.
If you have fine hulls you can use a lower Cp. Most monohulls have a Cp of 0.55- 0.57. And that is about right for displacement speeds. However the key to Catamaran design is you need a higher Cp if you want to sail fast. So a multihull should be at least 0.61 and a heavy displacement multihull a bit higher still.
T c = 0.57. Here we put B TR = 1.9 to minimize boat resistance (for her size) and get the draft calculation for a canoe body T c (Figure 1). Midship coefficient - C m. C m = A m / T c (x) B WL. We need to estimate a few coefficients of the canoe body. where A m is the maximum cross section area of the hull (Figure 3).
Hellkats Poweboats 32 catamaran. Just nine months ago, marine industry engineer Briland Hays—formerly with Contender Boats—and an investor purchased the assets of Miami-based Hellkats Powerboats.The fast-growing company was founded by the late Rey Marino.Its assets included tooling for 30- and 32-foot high-performance catamarans, as well as tooling for a 40-foot catamaran-hull-based center ...
2022 Custom 50 Feet Aluminium Catamaran. US$879,918. ↓ Price Drop. US $6,685/mo. Bach Yachting International | Dalmatia, Croatia. Request Info. Find Sail Catamaran Aluminum boats for sale in your area & across the world on YachtWorld. Offering the best selection of boats to choose from.
Betfred Super League. Hull KR (10) 26. Tries: Parcell, Hiku, Opacic, Sue, Burgess Goals: Lewis 3 Leeds (10) 16. Tries: Martin, Edgell, Ackers Goals: Martin 2